How A NRM Works?
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), as the name implies, is a technique for observing the activities of atomic nuclei of moleculars. By analyzing the characteristics of spin of the nuclei, the molecular structure is determined. Since the advent of technology of NMR in the 50's, NMR spectrometers have been used extensively in various research and applications of organic chemicals.
The principle of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is based on the characteristic of nuclear spin angular momentum. When the nucleus is applied to an external magnetic field, and its spin direction is opposite to the magnetic field, the atomic nucleus will swing around the direction of the magnetic field, as a gyro rotating. This phenomenon, which is so called precession. Precession has its energy, and a certain frequency. Besides, when the nucleus is placed in a constant magnetic field, this frequency will be a fixed value.

"Precession" Movement (From WikiPedia)
In addition, under the nucleus precession, the angle between the direction of nucleus magnetic moment and external magnetic field is not continuous, but the angle is jumped from one to another. Typically, one apply a RF field to provide the energy of this "jump", or so called "Resonance". The transition between one to another is related to the magnetic quantum number of specific nuclei. And it is not all of the nuclei has "resonance" capability. Those nuclei which have even number of proton and even number of neutron, has no resonance capability, such as O16, Ne20.
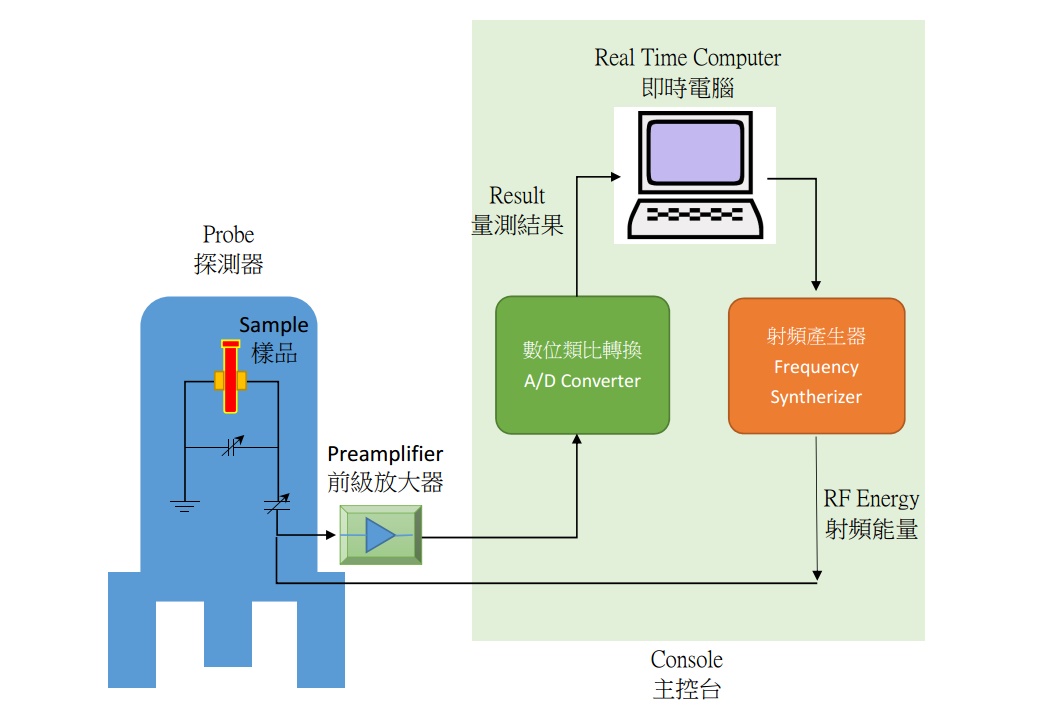
Therefore, a NMR spectrometer, uses the above principle, generate a constant external magnetic field onto the test sample, and impose a radio frequency energy on it, via a electric coil to detect the frequency of the nucleus spin precession (measured the electrical signals of the magnetic field, and by FFT, one can get the spectrum). And the the molecular structure can be determined.
The intensity of the applied magnetic field will influence the distance of each 'bar' in the spectrum. The larger the magnetic field applied, the longer distance can be get. And it is easier to observe the details of each frequency in the spectrum. But typically, a larger magnetic field means a larger volume of a NMR spectrometer. In the past, a large volume NMR spectrometer, typically needs a large room space, and the consumption of liquid nitrogen is also a heavy maintenance costs to some research organization.
In the recent years, by the developing of semiconductor technologies and the popularity of consumer electronics, some of high-SNR amplifiers and high resolution A/D converter are more popular and very cost effective. The advanced signal processing and signal analysis capabilities, is quite different than the past. It also led to the booming of desktop NMR. Some manufacturers had developed good desktop NMR spectrometers. And these NMR spectrometers are good enough for daily research and analysis jobs. Or the QC purpose of biochemical, pharmaceutical products in the quality control process. And the best thing is, the price of these desktop NMR are more friendly and acceptable cost, than the conventional huge NMR spectrometer.
ACTTR Technology brought to you the most advanced desktop NMR spectrometer products, for your daily education, research, quality control purposes, and bringing to you the effective, reliable, accurate and powerful tool.
For more NMR Spectrometer products, please visit ACTTR Product Page.


