How Can One Use ARCoptix IR Spectrometer for Transmission Measurement
The transmission FTIR sampling method is the most common and simple way in infrared spectroscopy. The infrared light is irradiated from one side of the sample, and transmit through the sample, and then be measured by the detector on the other side. Typically, researchers must made the sample into a tablet or film form factor, by the manual/automatic press . Prior to this, it requires IR matrix to be mixed and ground into powder (e.g. KBR).
The ARCoptix IR spectrometer series, presented by ACTTR in Taiwan, with rugged portability features. In addition to the advantage of USB power supply, compare to other brands of products, ARCoptix Rocket series also has with the Swiss state-of-art with the features of high-precision, calibration free benefits. Besides, it is an affordable FT-IR, FT-NIR, FT-MIR equipment for all the researchers with very good quality.
Read more: How Can One Use ARCoptix IR Spectrometer for Transmission Measurement
What Are The Common Applications In Using FT-IR Spectroscopy?
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) method helps researchers to analyze the chemical composition of materials and products, the scope covers the applications of consumer products, paints, polymers, surface coatings, pharmaceuticals, foods and the materials analysis for other products.
In organic and inorganic analysis, FT-IR is useful for the quantitative and qualitative analysis. It identifies the structure of molecules in a sample, via the infrared absorption spectrum. The spectra present the characteristics (light absorption) of each distinct molecule, and one can scan or screen various molecules. FT-IR is a useful tool for analyzing the functional groups or covalent bond structure of chemical compositions.
In addition, FT-IR can be used as a combination of other molecular spectroscopy methods, such as FT-IR coupled Thermogravimetric Analysis (FTIR/TGA), Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR), Gas Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS), Liquid Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS), UV/Vis Spectroscopy, Near Infra Red (NIR) and Raman Scattering. The combination of FT-IR and these spectroscopy technologies brought to the researchers the further complementary data for more reference and comparisons of molecular structure.
The FT-IR can be applied to the following applications areas:
- Quantitative & Qualitative Analysis
- The Materials of Solids, Liquids, Gases
- Organic Samples, Inorganic Samples
- Identification of Unknown Chemical Compound
- Impurities Screening
- Formulation, Deformulation
- Pharmaceuticals
- Paints, Surface Coatings, Laminates
- Polymers and Plastics
- Contamination Analysis
- Toxicity Screening
- Metals Analysis
- Gas Calibrations
What Is ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy?
Unveiling the Secrets Within: A Look at ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
Ever wondered what makes up the building blocks of our world? ATR-FTIR spectroscopy (Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy) is a powerful tool scientists use to unravel the mysteries of material composition.
Imagine shining a beam of infrared light onto a sample. In ATR-FTIR, this light interacts with a special crystal and the sample itself. As the light bounces back, some of it gets absorbed by the sample, revealing unique details about its chemical bonds and functional groups. By analyzing this infrared fingerprint, scientists gain valuable insights into the sample's:
Molecular Structure: How the atoms are arranged within the material.
Chemical Composition: The types of molecules present.
Chemical Properties: How the material might react with other substances.
Here's what makes ATR-FTIR spectroscopy so versatile:
- Non-Destructive: Samples remain intact, ideal for precious or delicate materials.
- Highly Sensitive: Even tiny amounts of a substance can be analyzed.
- Broad Applicability: Works with solids, liquids, and even pastes.
- No wonder ATR-FTIR is a favorite technique in various fields:
- Chemistry: Identifying unknown compounds, monitoring reactions, and ensuring product purity.
- Materials Science: Characterizing polymers, coatings, and other materials.
- Pharmaceuticals: Verifying drug composition and detecting contaminants.
- Environmental Analysis: Identifying pollutants in air, water, and soil.
- Forensics: Analyzing fibers, paints, and other trace evidence.
ATR-FTIR spectroscopy is a powerful workhorse in the scientific world, offering a non-destructive window into the molecular makeup of materials.

ATR-FTIR Equipment Is Compatible To All Desktop FTIR Spectrometer
A High Quality ATR-FTIR from SPECAC
What is penetration depth of ATR FTIR?
ATR-FTIR spectroscopy is a powerful analytical tool that provides detailed information about the surface chemical composition and structure of materials. It utilizes the principle of total internal reflection (TIR), where infrared light undergoes multiple reflections between a high-refractive-index crystal (e.g., diamond, germanium) and the sample, generating an evanescent wave that penetrates the sample surface.
Due to the shallow penetration depth of the evanescent wave, typically only a few micrometers, ATR-FTIR spectroscopy is particularly well-suited for analyzing thin films, coatings, and surface layers of materials.
How Does ATR Spectroscopy Work?
ATR (Attenuated Total Reflectance) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique that sheds light on the molecular makeup of materials. But how exactly does it work its magic? Let's delve into the fascinating world of ATR spectroscopy through the lens of SEO optimization and with some additional details to enhance understanding.
The Core Principle: Internal Reflection and Evanescent Waves
At the heart of ATR lies the concept of internal reflection. An infrared (IR) light beam strikes an ATR crystal (typically made of diamond, zinc selenide, or germanium) at a specific angle, exceeding the critical angle for the crystal material. This critical angle ensures the light reflects internally within the crystal instead of passing through it. Like the below figure:
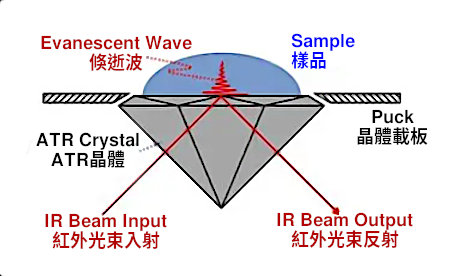
ATR Optical Mechanism
In order to ensure that the infrared beam will produce total reflection on the surface of the ATR crystal tip instead of transmission, the incident angle of the infrared beam must be greater than the critical angle of the crystal, and the critical angle depends on the refractive index of the crystal material. For example, the British SPECAC's QuestATR optical module is designed with a fixed incident angle of 45°, which is higher than the various ATR crystals that can be installed on this product, including diamond, zinc selenide (ZnSe) and germanium (Ge).
Evanescent Wave Adsorption
During the total reflection process, infrared light will penetrate to the interface between the crystal and the sample, forming an evanescent wave with a very short penetration depth. Due to the interaction between the evanescent wave and the sample, part of the infrared light is absorbed by the sample. The amount of infrared light absorbed is related to the molecular structure and composition of the sample. We can obtain the composition code of the sample molecules by interpreting the absorption values.
Technical Details of ATR Spectroscopy
Angle of Incidence: The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle to ensure the light beam reflects from the ATR crystal surface rather than transmitting through it. The critical angle depends on the refractive index of the crystal material.
Evanescent Wave: The Evanescent Wave is a key concept in ATR spectroscopy. It has a very short penetration depth, typically only a few micrometers, which makes it highly sensitive to the sample.
ATR Crystals: The choice of ATR crystal can significantly impact the quality of the spectrum. Common ATR crystal materials include diamond, zinc selenide, and germanium.
Sample Preparation: ATR spectroscopy has minimal sample preparation requirements. Solid samples can usually be placed directly on the ATR crystal. Liquid samples can be spread onto the ATR crystal or placed in an ATR cell.
Specac, the designer and manufacturer of accessories and sample preparation solutions in UK, has brought to you the disposable Arrow Silicon ATR slides, which is a perfect solution to those senstive precious samples. This product can avoid interpollution between samples. It is the best solution for biochemical, pharmaceutical research applications.
Conclusion
ATR spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique that offers valuable insights into the molecular composition of materials. Its non-destructive nature, high sensitivity, and broad applicability make it an indispensable tool in various scientific fields, including chemistry, material science, pharmaceuticals, environmental analysis, and forensics. As technology continues to advance, ATR spectroscopy is poised to play an even more prominent role in our understanding of the world around us.
We have many other special ATR solutions for your research & experiments, such as very low temperature ATR equipment. You're welcome to contact ACTTR Technology, and we're pleased to serve you.

-150°C Very Low Temperature ATR Equipment


