The Importance of Particle Characteristics in Metal 3D Printing
In metal 3D printing, Particle Size Analysis is a critical step in ensuring high-quality manufacturing. By leveraging advanced Particle Size Analyzers, industries can achieve superior control over powder characteristics, leading to enhanced print precision, improved mechanical properties, and greater overall efficiency in additive manufacturing processes. As 3D printing technology continues to advance, the role of particle analysis in optimizing material performance will remain indispensable.
Read more: The Importance of Particle Characteristics in Metal 3D Printing
Evaluating Hiding Power of Pigments by A Particle Size Analyzer
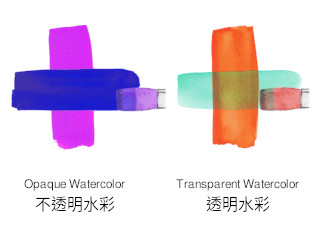
The "Hiding Power" of a pigment, also known as hiding strength or coverage, refers to the capacity of a coating or pigment to conceal the underlying surface or previous layers, effectively obscuring the color or pattern of the substrate. When we paint the wall or paintings layer by layer, the top layer of pigment can effectively cover the original color in the lower layer. Take watercolor painting as an example, when we applying opaque watercolor onto an existed color block, it can easily cover the underlying color (opaque watercolor has stronger hiding power), while the transparent watercolor cannot completely cover the lower layer, but it results the artistic effect of color layering or gradient (weak covering power).
The hiding power of pigments are of great significance to the manufacturing industries of paints, art paints, printing, etc., because it determines the ability of covering the surfaces with blemishes or dirt (opaque requirements), or to achieve gradual ability to layer artistic effects (semi-transparent requirements).
Read more: Evaluating Hiding Power of Pigments by A Particle Size Analyzer
Monitor The Degradation of In-Service Lubricants by FT-IR

Lubricants is mainly used for lubrication inside the machine, as well as the functions of cooling and anti-rust. For example, the lubricants in an engine is an indispensable substance for its normal operation. When the lubricant gets aged and deteriorated, it will cause metal wear on the high-speed running parts inside the engine, and even cause damage to the cylinder or piston. Leading to a car, motorcycle, or aircraft stalling, even more serious consequences.
Read more: Monitor The Degradation of In-Service Lubricants by FT-IR
Improving Electrode Slurry Quality by Using BeNano Zeta & Particle Analyzer

The manufacturing process lithium battery electrodes involves the mixtures of electrode active materials, binders, additives, and solvents. These materials are mixed together and finally forming into a slurry style, which is used to be coated on the electrode metal substrate. After the final drying process and removing the solvent, the metal substrate will be pressed and molded into the final battery electrode form.
The process of preparing electrode slurry is complicated. The slurry must be within a certain viscosity range and maintain stability for a long time. If the substances in the slurry settle or lose their viscosity during the production, it will cause problems in the later coating and drying/baking processes. A bad quality slurry may even cause the entire batch of electrodes failed. Therefore, in the front-end process stage, the quality of the slurry needs to be strictly controlled. The highly automated and high-performance "BeNano Particle Size & Zeta Potential Analyzer" is the best tool for process quality control.
Read more: Improving Electrode Slurry Quality by Using BeNano Zeta & Particle Analyzer


