The Optical Basics of Spectroscopy
Wave Behavior of Light
Radiation is a form of energy. The human body feels its existence via vision (visible light) and sensory (heat). Radiation is a wave phenomenon, which is generated by electromagnetic effects. in the nature world, people refer to all of the energy fluctuations as "electromagnetic radiation The human eyes can see "visible light", and it is also a kind of electromagnetic wave.
After successive experiments, the scientists have confirmed that radiation, light, electromagnetic waves, are exactly the same kind of thing. They are a kind of energy, and scientists found the wave behavior of energy by the experiments of light diffraction. In order to explain the appearance of electromagnetic waves, scientists usually use sine wave. It looks, as shown below:
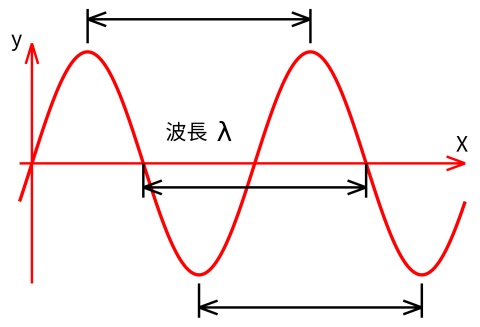
The waveform of electromagnetic waves
Electromagnetic wavelength, λ, is on behalf of the distance between two peaks; and the frequency, ν, is the times of peak, which passed a fixed point within one second.
The unit of wavelength is usually nanometer (nm), millimicron (mμ), or Angstrom (Å). The conversion among these units are as follows:
1 nm = 1 mμ = 10-9 meter
1 nm = 10 Å
The unit of frequency is typically Hertz (Hz, Hertz), as well as Kilohertz (KHz), Megahertz (MHz), Gigahertz (GHz), and the conversion of these units are defined as follows:
1KHz = 1000Hz
1MHz = 1000KHz
1GHz = 1000MHz
Multiplying both wavelength and frequency, we can get the electromagnetic wave speed v (velocity). The relationships among these 3 values can be expressed as the following equation:
v = νλ
In the medium, the velocity will be slower than the speed of light, c. However, in a vacuum, the velocity, v, is equal to the speed of light, c. The formula can be adjusted as follows:
c = νλ
For example, the broadcast frequency of the radio station, “News98”, is 98.1MHz. By the light speed of 300,000 kilometers per second (300 million meters), we can estimate the wavelength of “News98” radio signal is about 3 meters. (300,000,000 m / 98.1M = 3.0581m).
Particle Behavior of Light
The scientist, Planck (Max Planck), proposed the “Planck's Quantum Hypothesis” of electromagnetic energy on December 14, 1900. He explained the defects of blackbody radiation formula by Wien & Rayleigh, and that the energy of the electromagnetic wave. There is a fixed frequency ratio can be expressed in the following equation:
Ε = hν
The energy Ε (epsilon) of joules, ν (neu) is the frequency, h is Planck's constant (6.626 × 10-34 Js).
Further, in the black body radiation, the energy will only be an integer multiple of hν. In other words, it is:
Ε = 0, hν, 2hν, 3hν, 4hν, ..., nhν
Later, after the experiment of Einstein's photoelectric effect, he further proved the reliability of the Planck constant. In his experiments, he designed three variable parameters:
1. Photoelectric conversion current (i), that is, the intensity of light, or that the number of photons.
2. Blocking voltage (V), is used to generate deter potential (V0), which stops the light current.
3. Optical frequency (ν)
By fixing the two parameters, V and ν, and adjusting the intensity of light, Einstein found that the amount of the photocurrent, is proportional to the light intensity, with linear relationship. Further, by controlling the blocking voltage, he found the electron energy which is required, only related to the frequency of the light, instead of the intensity. Besides, the blocking voltage is proportional to the frequency light. And the slope exactly equals to the Planck constant.
Thus, the intensity of light is related to the amount of photons, rather than the energy of the light.
By collecting all the different continuous electromagnetic wavelengths together, we get a "spectrum". Scientists divided the spectrum into several segments, and gave each segment a unuque name. "Visible" segment is the one that the human eyes can read. The wavelength of Visible segment starts from red color and ends to purple color. The wavelength of red light is longer, and the wavelength violet light is shorter.
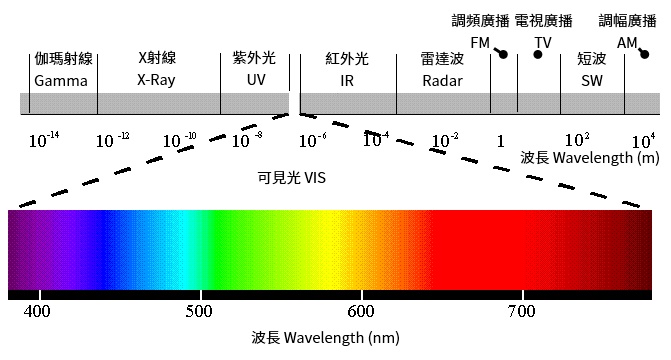
Each Segment in The Spectrum
Spectroscopy & Spectrometer
Spectroscopy is the subject of the electromagnetic radiation energy of material. The focused electromagnetic wavelength is between the range of Gamma Rays to Microwaves. By the definition of SAS(Society for Applied Spectroscopy), the standard wavelength of each segment is defined in the below table:
|
Segment |
Wavelength (nm) |
|
Far Ultraviolet |
10-200 |
|
Near Ultraviolet |
200-380 |
|
Visible |
380-780 |
|
Near Infrared |
780-3,000 |
|
Middle Infrared |
3,000-30,000 |
|
Far Infrared |
30,000-300,000 |
|
Microwave |
300,000-1,000,000,000 |
A more detailed definition and table defined by ISO (International Organization for Standardization) can be downloaded here.
Because the visible light, ultraviolet light, and infrared light are relative easy to be obtained and observed, the UV / visible / infrared (UV-Vis-IR) spectroscopy technologies are the earliest developed technology.
The principle of a spectrometer is irradiating a light sensor (photoelectric converter) by use of a light source. According to the energy measured by the light sensor, one can obtain the photon number received by the sensor in a time interval. If we set up the sample in between the light source and light sensor, the sample will absorb part of the photons. And the sensor will receive fewer photons, thus reducing the amount of energy measured from the sensor. So that we can calculate the difference between the origin and the result. By this analysis, one can realize the characteristics of the sample.
Light source is a consumable component in the spectrometer, as the lamp on your desk. There is a certain life cycle. An artificial light source in a spectrometer is typically a tungsten lamp, which is the most common light source, and the wavelength range of light, covers the entire visible light wavelength range. Tungsten lamp is widely used in a visible spectrometer, to be the light source . Deuterium lamp (also known as the D2 lamp), which has wavelength in the UV light range, and therefore it is a common light source of a UV spectrometer.
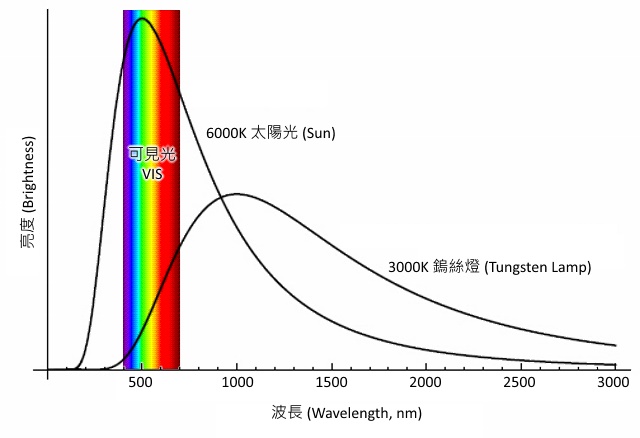
Tungsten Light Source
Scanning type spectrometer (For example, UV-Vis Spectrometer Series of ACTTR Technology). It scans entire range of the spectrum, generate the graph of spectra. According to the result spectra, one can observe the energy status of each wavelength measured. And one can understand the characteristics of the sample preciously. UV-Vis Spectrometer is becoming the most common and inexpensive spectrometer equipment. It is affordable in many different kind of applications.


