What ARC Can Tell You in HWS Cycles
What is HWS?
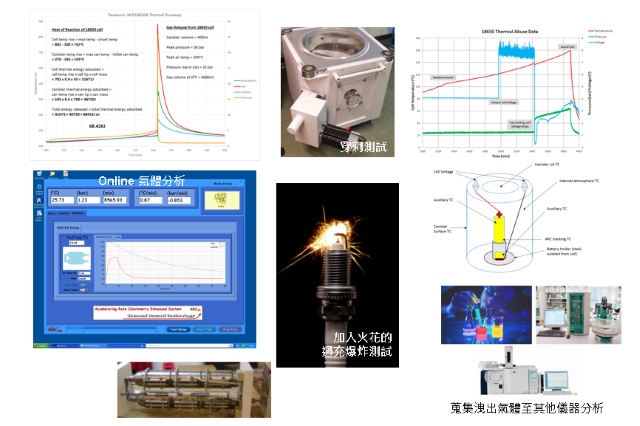
HWS means heat-wait-seek, it is the 3 processes in which ARC can monitor the reaction of the battery. ARC heats to the start temperature, waits for temperature equilibration, then seeks the exotherm. This loop continues until a reaction is found (self-heat rate exceeds sensitivity threshold) then the ARC switches to EXOTHERM mode.
Exotherm mode tracks the reaction and maintains an adiabatic environment, until the reaction is finished. Take the below figure for example, it is an typical HWS cycles. In the 4th cycle, there is an abnormal reaction, the final temperature is obviously over the given energy. ARC starts the EXOTHERM mode immediately. And in the 5th cycle, the battery is over heat and going into out-of-control situation.
What ARC Can Tell You?
Compare to the result that Samsung Galaxy Note 7 was tested in Singapore (Applied Energy Hub battery laboratory), ARC belongs to different level of measurement. ARC is able to provide more detailed data, and help the researchers to find the real hidden problem of the design. And avoid the accidents happen or modify the design of the products. The result of testing in Singapore is a more roughly testing. It shows the damage and explain the damage under a certain stress, but it cannot explain the reason, either from internal short circuit, or the damage of separates inside the battery. Probably, the mobile phone burning in the experiment was caused by the external short circuit, when the rod looks like a metal rod in the photo. By the HWS process of ARC measurement, user can really find out the reason of defective. Of course, ARC can also measure the exotherm result along with the electrical control or other physical operations, such as the nail penetration function, which is able to simulate the similar experiment as the one in Singapore.
Below are some examples to show you what the functions that ARC can provide your the useful analytical information and test results:
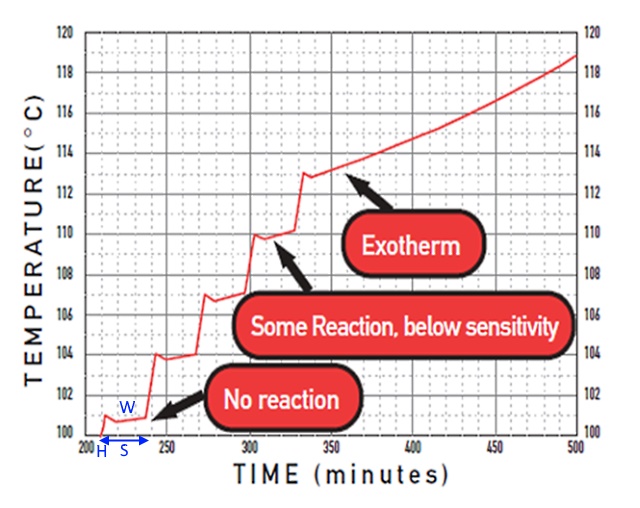
A. Exotherm onset and time
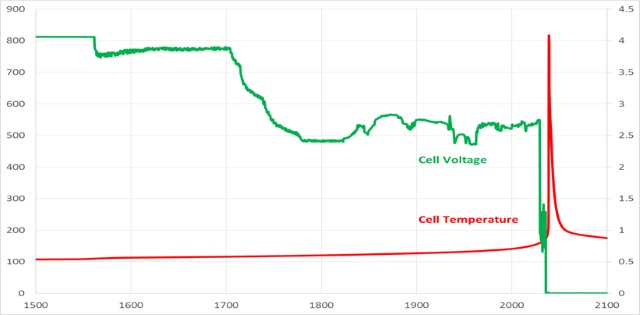
B. Voltage against temperature
C. Heat of reaction
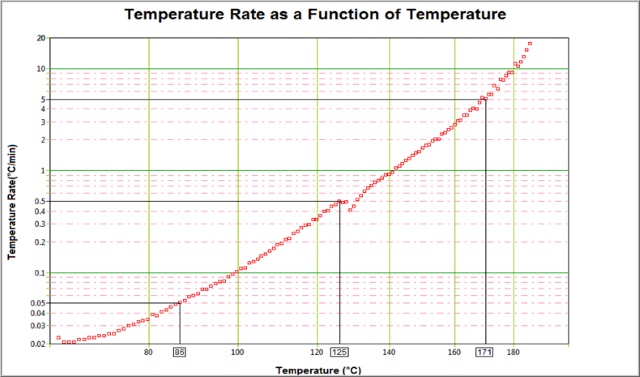
D. Venting temperature
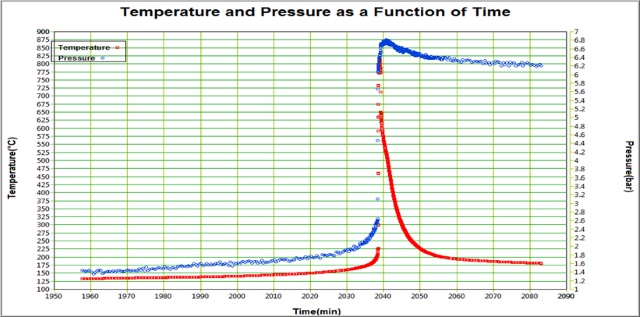
E. Separator Melting Temperature
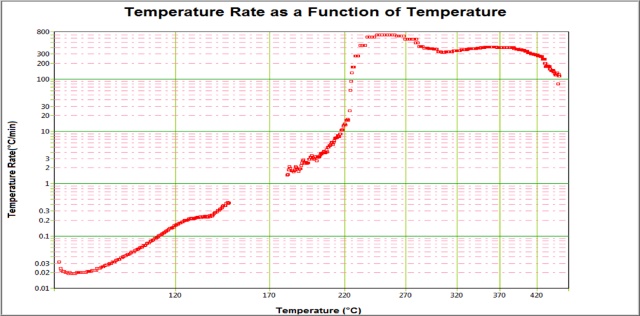
According the above functions, the researchers can simulate many different situations, conditions, along with various electric methods or physical methods (like the one in Singapore). Via the HWS process and thermal analysis, one can find out the potential design problem. In the same time, the researcher can understand the limitation of the battery under the extreme conditions under the natural or artificial operations. And find out the potential risk as early as possible, in order to avoid the accidents, reduce the economical loss to the minimum.